Immunological Forgetting
Immunological Forgetting
Blog Article
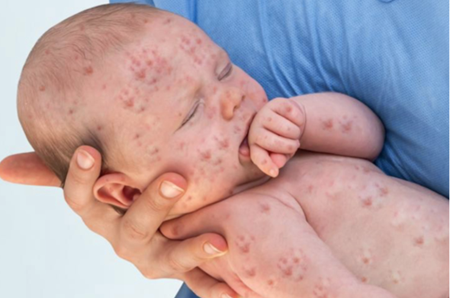
Immune amnesia, commonly termed as immunological forgetting, explains the phenomenon where the immune system struggles to remember previous exposures with specific pathogens. This complex process occurs when the immune system undergoes a change, resulting in an greater risk to reinfection.
- Several factors can contribute to immune amnesia, including certain illnesses and the use of therapy that weakens the immune system.
- Understanding immune amnesia is highly important for finding novel solutions for a wide range of infectious diseases.
Grasping Immune Amnesia: Causes and Consequences
Immune amnesia is a complex phenomenon where the immune system seemingly fails to remember past encounters with pathogens. This condition can occur due to various factors, including stress.
The implications of immune amnesia can be significant. Patients may become susceptible to recurrent diseases, even those they have previously defeated.
Moreover, understanding the processes behind immune amnesia is crucial for developing innovative therapies and strategies to mitigate this complex health issue.
The Intricate Connection Between Measles Virus and Immune Amnesia
The measles virus, a highly contagious pathogen, has long been recognized for its ability to trigger a range of debilitating symptoms. However, recent research has shed light on a more complex aspect of this virus: its potential to here cause immune amnesia. This phenomenon, characterized by the diminution of immunological memory following infection, poses a substantial threat to long-term resistance.
The precise mechanisms underlying this connection remain under investigation. Some studies suggest that the measles virus may directly attack immune cells responsible for memory, while others posit that its inflammatory response could degrade the overall immune system.
The implications of immune amnesia are far-reaching. Individuals who develop this condition may become more susceptible to a broad range of infections, even those they have previously been exposed to. This vulnerability can persist for decades, highlighting the need for ongoing research and awareness.
Immune Amnesia Definition: Explaining the Phenomenon
Immune amnesia is a complex and fascinating phenomenon that describes the inability of the immune system to recognize previously encountered pathogens. This condition occurs when the body's ability to produce antibodies against specific agents is impaired or lost. As a result, individuals may become vulnerable to repeated infections from pathogens they have previously encountered. Immune amnesia can be caused by various factors, including certain therapies, viral infections, or genetic predispositions.
- Understanding the mechanisms behind immune amnesia is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent its occurrence and treat its consequences.
- Research into this phenomenon continues to unravel the complex interplay between the immune system and pathogens, shedding light on the intricacies of human health and disease.
How Measles Affects Immune System Retention
Measles virus infection can have a significant effect on the immune system's memory. While measles vaccination effectively protects against this highly contagious, natural episodes of measles can compromise a person's power to create immune responses laterdown the road. This is because the virus has the likelihood to attack immune cells responsible for {recognizing and fightingpathogens.
Rebooting the Immune System
The concept of immune amnesia, where the body may forgets past infections, is a curious one. This imagined reset may shed light on the body's ability to adjust to new enemies. While the systems behind immune amnesia are still being studied, it offers a uncommon outlook on how our immune network operates.
- Potentially the immune system purges past infections, allowing it to zero in on current threats.
- This reset may account for the recurring nature of some diseases, as our defense fades.
Your Wiki Guide : Your Source for Information on Immune Amnesia
Immune amnesia is a process in which the immune response forgets past encounters to pathogens. This can occur during certain medical treatments, such as bone marrow grafting. Understanding immune amnesia is crucial for researchers working in the field of immunology.
- Wikipedia provides a comprehensive overview of immune amnesia, including its causes, manifestations, and potential management strategies.
- Furthermore, Wikipedia offers references to scientific journals, allowing you to delve deeper into the topic.
Dissecting the Mysteries of Immune Forgetting
Immune amnesia, a puzzling phenomenon where/in which/that the immune system seems to forget/lose track of/fail to remember past infections/exposures/encounters, has long been/remained a mystery for/baffled scientists. This loss/absence/disappearance of immunological memory can lead to/result in/cause individuals becoming susceptible/vulnerable/prone to the same illnesses/diseases/conditions multiple times, even after previous recovery/experiencing a past bout/being treated for them. Researchers are actively investigating/diligently pursuing/keenly exploring various theories/hypotheses/explanations to understand/explain/elucidate this intriguing phenomenon/occurrence/conundrum. Some studies/researchers/investigations suggest that immune amnesia may be linked to/associated with/connected with factors such as viral infections/immune suppression/genetic predisposition, while others propose/suggest/hint at a role for the aging process/wear and tear on the immune system/decline in immune function.
Lost Defenses: The Consequences of Immune Memory Loss
Immune amnesia, a troubling phenomenon where the immune system forgets past infections, has profound implications for global safety. While our adaptive immunity typically builds a detailed library of pathogens, immune amnesia undermines this essential protection.
The ramifications of this loss can be grave, leading to a repeated vulnerability to previously encountered diseases. Moreover, immune amnesia could hinder the effectiveness of vaccines, likely rendering them unsuccessful against previously contained infections.
- Researchers are actively investigating the mechanisms behind immune amnesia, seeking to unravel its complex character.
- Potential contributors include environmental toxins, which could impair the immune system's ability to preserve memory of past illnesses.
Immune Amnesia?
Immune amnesia, a perplexing phenomenon where the immune system forgets past exposures to pathogens, is emerging as a potential public health threat. This decline in immunological memory can result individuals to become susceptible again to diseases they have previously overcome. The origins of immune amnesia are multifaceted, including aging, underlying medical conditions, and certain drugs. Unraveling the mechanisms behind this phenomenon is vital for developing effective approaches to mitigate its impact on public health.
Research Frontiers in Immune Amnesia
Recent substantial advances in immunology have unveiled fascinating new insights into the enigmatic phenomenon of immune amnesia. This complex state, characterized by the partial loss of immunological memory following defined infections or therapeutic interventions, poses unanswered questions about the persistence of immune responses. Researchers are actively probing novel pathways underlying immune amnesia, aiming to clarify its origins.
Promising progress is being made in understanding the role of molecular factors that contribute to this phenomenon. Moreover, investigations into the epigenetic modifications associated with immune amnesia are shedding light on its reversibility for restoration. This burgeoning field holds immense possibility for developing novel therapies to manage immune-related disorders and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Report this page